Deploying Microsoft Dynamics NAV on Azure: Performance best practices for four architectures
When talking about deploying Microsoft Dynamics NAV for a customer, nowadays you have four options available for your architecture.
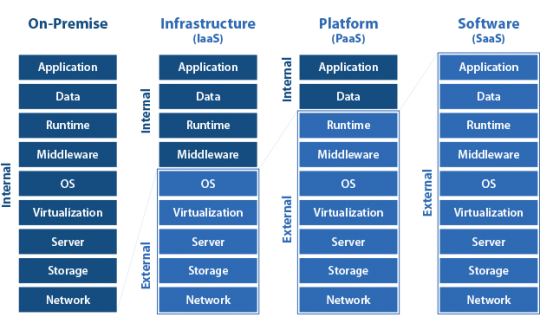
- On-Premises: You manage everything, from hardware to software. This is the most common way to deploy Microsoft Dynamics NAV.
- IaaS: You hand over the infrastructure management to someone else, in this case, the Azure cloud, and you need to manage the database, and the server setup. In terms of Azure, this is NAV deployed by using VMs.
- PaaS: Here, the database layer is managed by someone else, and you have to think only about data, and application layers. In terms of Azure, this is NAV deployed by using Azure SQL Database.
- SaaS: Infrastructure and applications are managed by someone else. You activate a service and you're ready to go. This is the Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central service model.
In this article, we will focus on IaaS and PaaS, how to deploy Dynamics NAV on Azure, and the best practices for a successful implementation.
Dynamics NAV on Azure Virtual Machines
When you want to deploy Dynamics NAV on Azure in an IaaS model, automatically you think of Azure Virtual Machines (VMs). Azure VMs provide on-demand, high-scale, secure, virtualized infrastructure using Windows Server.
When you plan to create a solution architecture with Dynamics NAV deployed on Azure VMs, you have essentially two main topologies:
- Option 1: NAV Service Tier and SQL Server on the same Azure VM
-
Option 2: NAV Service Tier and SQL Server ...
FREE Membership Required to View Full Content:
Joining MSDynamicsWorld.com gives you free, unlimited access to news, analysis, white papers, case studies, product brochures, and more. You can also receive periodic email newsletters with the latest relevant articles and content updates.
Learn more about us hereor login